
Geodivesity Day at a transnational geopark 09/13/2024 8:17 AM
- News
- Geodivesity Day at a transnational geopark
Geodivesity Day at a transnational geopark

- News
- Geodivesity Day at a transnational geopark
October 6 is the International Geodiversity Day, celebrated worldwide by UNESCO. In order to Conserve the Past and Sustain the Future, the rich repository of the geological heritage of the transnational, Slovak-Hungarian Novohrad-Nógrád UNESCO Global Geopark will also join the event. On the traditional geotope days, October 5th and 12th, from the state border area to Ipolytarnóc and from Sámsonháza to Szentkút, it organizes many exciting and unconventional geotours into the world of volcanoes of the past.
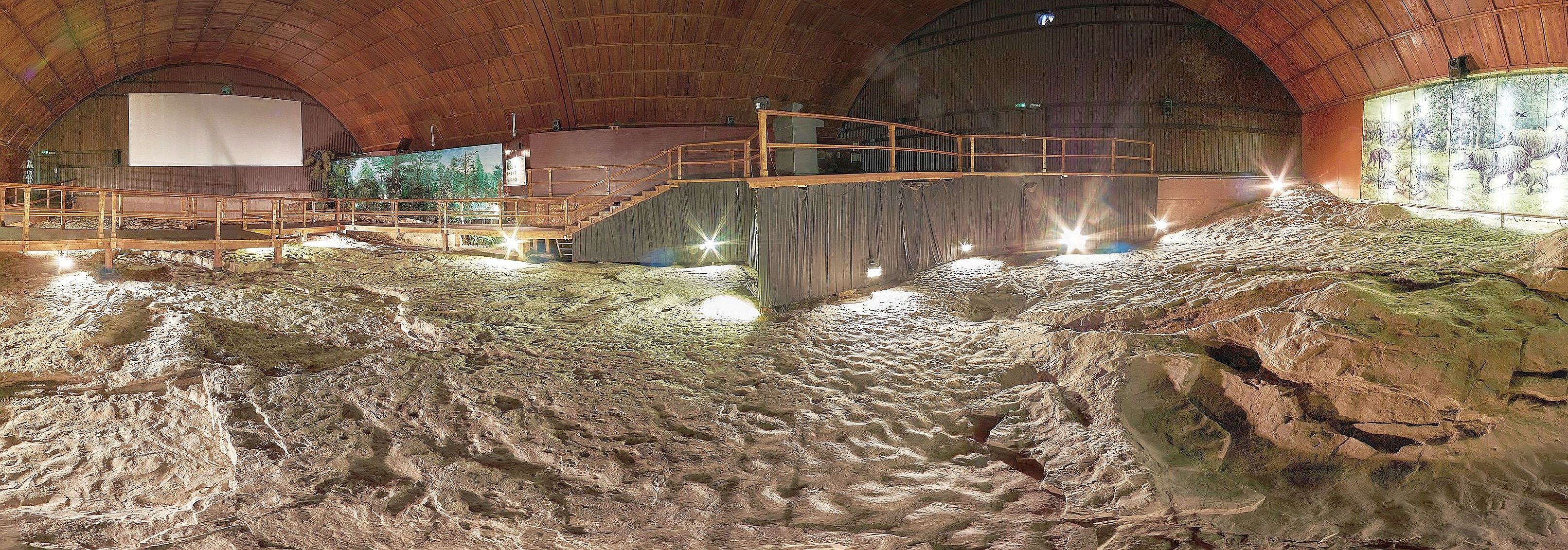


In the Miocene Park of the Ipolytarnóc Fossils geosite, a thematic tour will be organized on October 5, the details of which, along with the background of the geodiversity day, can be found at this link.
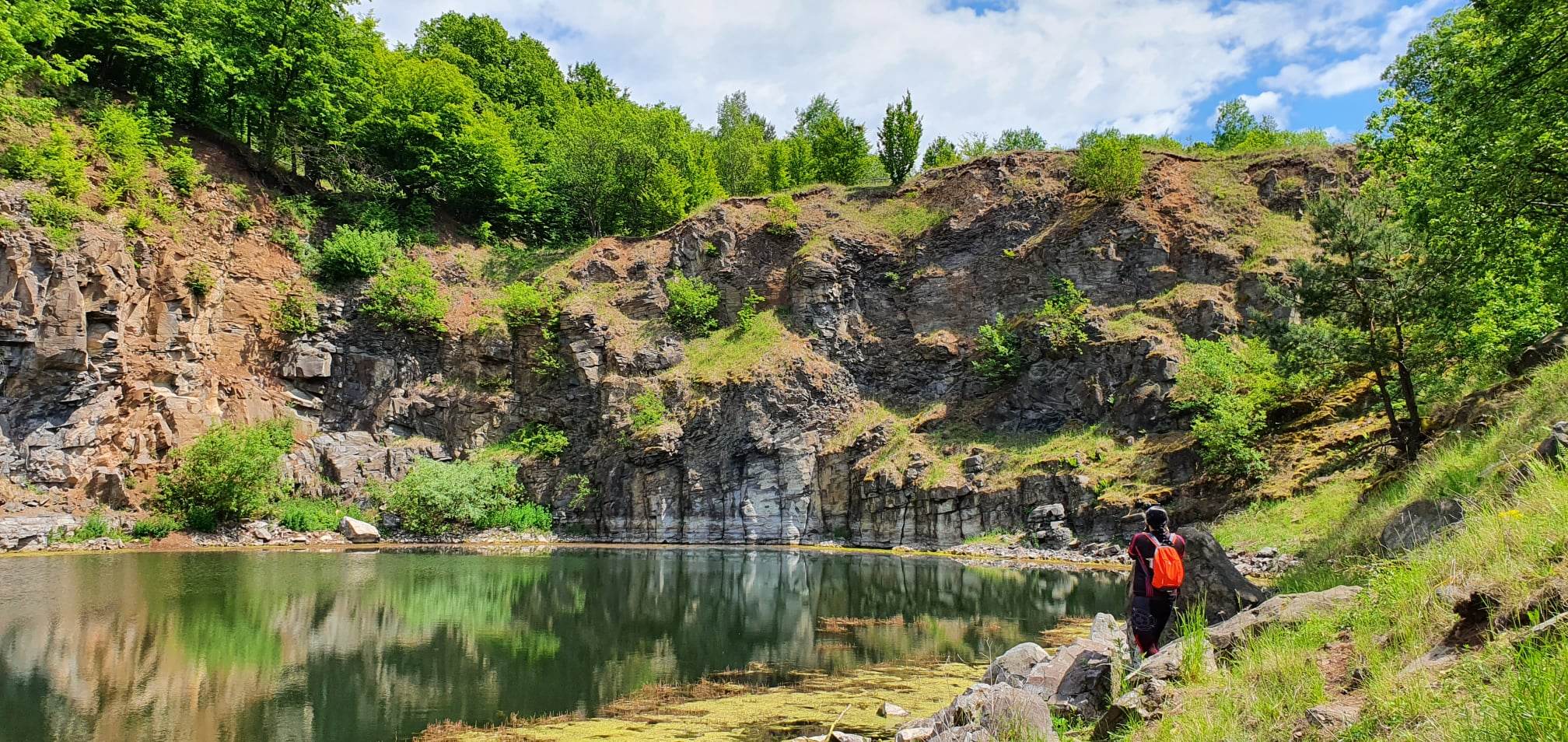

Also on October 5, at 10:30 a.m., a special 10 km long tour to the basalt region of the Medves Plateau will start from the Eresztvény Visitor Center of the geopark, during which the participants will learn about the geohistory and mining of the picturesque landscape, while visiting several reclaimed quarries. You can participate in the tour free of charge, pre-registration can be done by sending a message to the email address info@nngeopark.eu or by calling the landline +36 32 423 303.
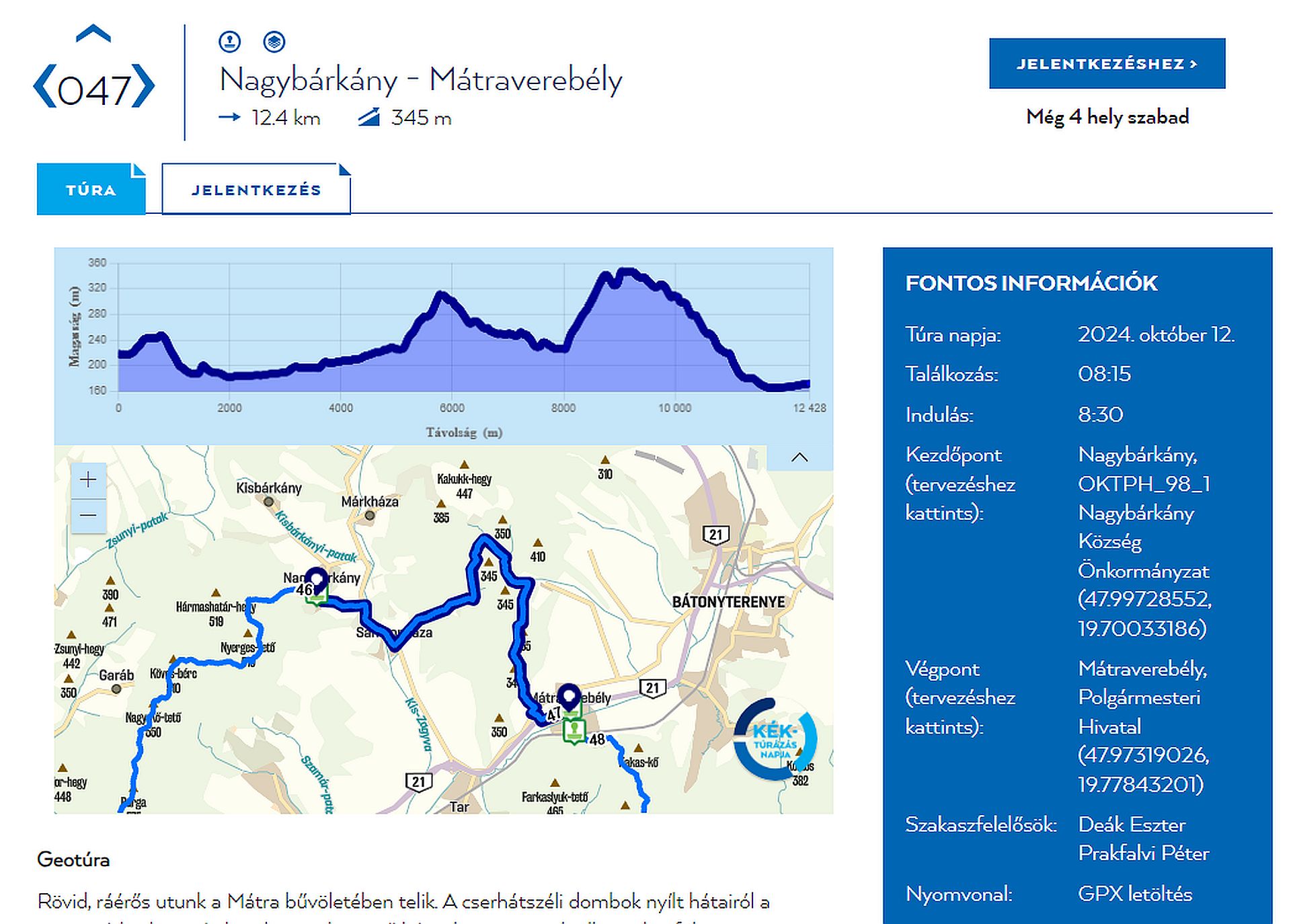
And on October 12, the chief geologist of the geopark, Péter Prakfalvi, will lead an interesting tour in the Cserhát mountain, which starts at 8:30 a.m. from the Municipal Hall of Nagybárkány. The tours goes to the startovolcano of Samsonhaza and ends at the pilgrimage site of Szentkút. The exact details of the 12.4 km long tour are described on the Kéktúra website.

- Visitor centers
- Novohrad-Nógrád Geopark
- Családoknak
- Geological
- Időseknek
- Nógrád
- nogradgeopark.eu
- Fiataloknak
- Geological section
- Karancs-Medves Protected Landscape Area
- osmaradvanyok.hu/en
- World Heritage site
- East Cserhát Protected Landscape Area
- European Diploma
- Sacral heritage
- Túra
- Múltbeli érdekességek
- Guided tours
RELATED















